- 翰林提供學(xué)術(shù)活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學(xué)背景提升服務(wù)!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel化學(xué)往年真題考點詳解(1)
馬上就要到暑假了,同學(xué)們高興之余也不要忘記學(xué)習(xí)哦,為了幫助同學(xué)們更好地鞏固所學(xué)知識,今天我們通過幾道真題,給大家回顧一下所學(xué)的重點知識。
1.??Compounds A and B are isomeric alkenes.
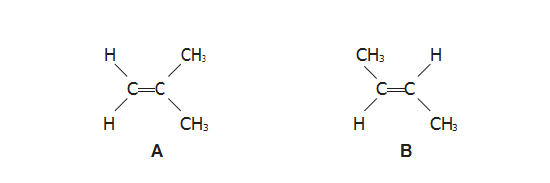
(a)(i) Name compound A.
【答案】:2-methylprop-1-ene
【分析】:這道題主要考察的是烴類的命名。
對于烴類(hydrocarbon)的命名我們的答題方法是:
第一步選主鏈,主鏈的選擇原則是選含官能團(tuán)(functional group)在內(nèi)的最長的碳鏈為主鏈,本題中包含雙鍵(double bond)在內(nèi)的最長碳鏈有3個碳且含有雙鍵所以他是一個propene。
第二步定編號,編號原則是官能團(tuán)(functional group)和取代基(substituent group) 位次最小(官能團(tuán)優(yōu)先排序)。所以應(yīng)從左邊的碳開始排序,在二號碳的位置有一個甲基所以是2- methyl,雙鍵起始于第一個碳所以是1-ene
所以,這道題的答案是?2-methylprop-1-ene
(ii) Give the molecular formula of compound B.
【答案】:C4H8
【分析】:回答這道題時,應(yīng)體現(xiàn)出物質(zhì)所有的元素以及所有元素所含原子的真實個數(shù)。
(iii) Explain why A and B are isomers.
【答案】:A and B have the same molecular formula but different structural formula
【分析】:這道題考察的是同分異構(gòu)體的概念。
具有相同分子式而結(jié)構(gòu)不同的化合物互為同分異構(gòu)體(isomers)。A,B兩種物質(zhì)甲基在雙鍵碳的不同位置,所以他們互為同分異構(gòu)體(isomers)。
(iv) Draw the geometric isomer of compound B.
【答案如圖】:
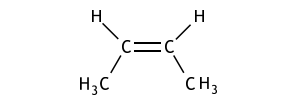
【分析】:由于雙鍵的不可旋轉(zhuǎn)當(dāng)不同級別的官能團(tuán)連在雙鍵碳的同側(cè)和異側(cè)時會產(chǎn)生順反異構(gòu)
(geometric isomer)。
(v) Explain why compound B has a geometric isomer but compound A does not.
【答案】: There?are two different groups bonded to each of the carbon atoms of the double bond in compound B
【分析】:只有雙鍵碳兩邊連接的是不同的官能團(tuán)時雙鍵碳才有幾何異構(gòu)體(geometric isomer)。
(b)?Compound C is an isomer of compounds A and B. Some reactions of compound C
are shown below.
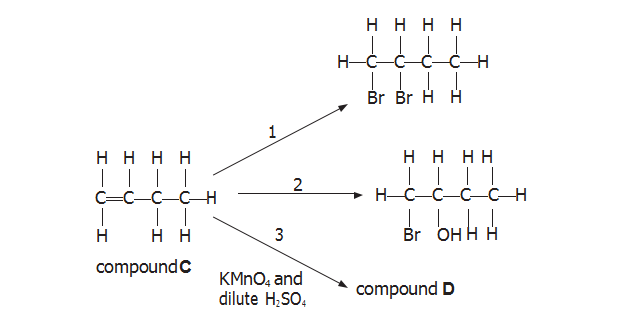
(i) Name the reagent(s) required for reaction 1.
【答案】:bromine
【分析】:烯烴的加成(addition ) 反應(yīng),雙鍵斷裂與鹵素加成生成鹵代烴(halohydrocarbon)。
(ii) Name the reagent(s) required for reaction 2.
【答案】:?Bromine water
【分析】:烯烴須鹵素溶液的加成,鹵素和羥基(hydroxy)分別加到雙鍵兩側(cè)。
(iii) Draw the displayed formula of compound D.
【答案如圖】:
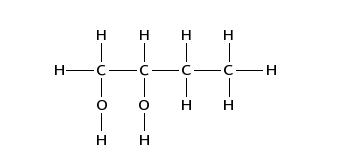
【分析】:烯烴在KMnO4 and dilute H2SO4條件下會發(fā)生加成反應(yīng)生成鄰二醇。
(C) Compound C also reacts with hydrogen chloride.
(i) Classify the type and mechanism of this reaction.
【答案】:Electropic Addition
【分析】:當(dāng)烯烴相與HX和水反應(yīng)生成鄰二醇的時候,先加成生成一羥基鹵代烴在取代生成鄰二醇。
2 .?The table below shows the experimental and calculated values for the lattice energy of sodium chloride and silver chloride.
| Compound | Lattice Energy / kJ mol?1 | |
| Experimental | Calculated | |
| sodium chloride | ?780 | ?770 |
| silver chloride | ?905 | ?833 |
(i) Write the equation for the lattice energy of sodium chloride. Include state symbols.
【答案】:Na+(g) + Cl (g) → NaCl(s)
【分析】:晶格能(lattice energy) 也可以說是破壞1mol晶體,使它變成完全分離的氣態(tài)自由離子所需要消耗的能量。
(ii) Name the energy cycle used to calculate lattice energies from experimental data.
【答案】:Born-Haber (cycle)
【分析】:送分題,很明顯答案是?Born-Haber (cycle)
(iii) Explain fully why the experimental and calculated values for the lattice energy of sodium chloride are similar, whereas those for silver chloride differ significantly.
【答案】:Sodium chloride is purely ionic, Silver chloride is partly covalent,
so small(er) electronegativity difference between Ag and Cl.
【分析】:因為鈉和銀之間的電負(fù)性相相氯和銀之間的電負(fù)性(electronegativity)要大。
今天講解的兩道題分別考察了有機(jī)物和無機(jī)物中的相關(guān)知識點:
烴類的命名
有機(jī)化合物的分子式
同分異構(gòu)體的概念
幾何異構(gòu)體的概念
烯烴的加成反應(yīng)
晶格能的概念和影響因
伯恩哈勃循環(huán)

最新發(fā)布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









